Counting bacteria
Bacteria can be counted in different ways, and here are three fundamentally different methods:
- Determination of CFU (Colony Forming Unit). Samples that should be analysed are diluted and spread on/in agar plates, which are incubated under different conditions depending on the method for analysis, i.e. which bacteria could be expected from the current issue. This method is relatively accurate, provided that the dilution is performed in a proper manner and that the bacteria do not form aggregates in suspension cultures. Disadvantage: the answer is obtained after at least 24 h depending upon which agar is used and which bacterium you look for. See also Colony Forming Unit.
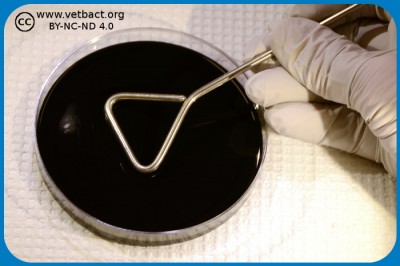
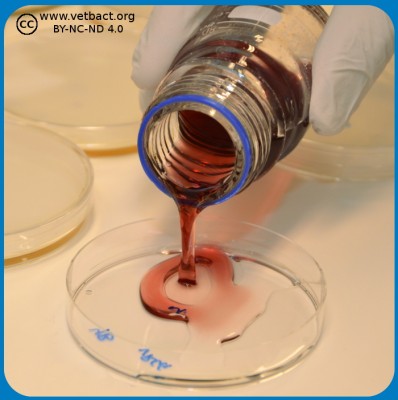
Depending upon test parameter, surface spreading or pour plate technique is used in food microbiology. A ten-fold serial dilution is prepared and for surface spreading, 0.1 ml is used from the different dilutions and 1.0 ml is used for pour plating. In surface spreading 0.1 ml from the dilution is distributed by a sterile spreader on the whole agar surface (see Fig. 1). However, in pour plating, the bacteria are directly mixed in the whole volume of the "melted" agar in the petri dish (see Fig. 2) and not only on the surface. The melted agar has a temperatur of 45°C, which does not kill the bacteria, but keeps the agar fluid.
- Spectrophotometric determination of light scattering. The method provides a relative measure of the number of bacteria, but can be calibrated with a standard curve. See Growth Curve.
- Direct counting in a so called Bürkner chamber that can be placed under a microscope. The method is relatively uncertain and is not used that often.
Updated: 2020-02-13.
|